Establishment

Establishment of Faisal Islamic Bank
The notion of establishing Islamic banks began in the mid-seventies, where it started with the establishment of the Islamic Development Bank in Jeddah, followed by a public effort especially to establish Islamic banks where His Highness Prince Mohammed Al-Faisal was the pioneer in calling for the establishment of Islamic banks starting with Dar Al-Maal Holding Company, with a capital of billion dollar which established many Islamic banks in a number of countries.
Sudan was not far from these efforts; indeed, the idea of establishing an Islamic bank in Sudan first emerged at Omdurman Islamic University in 1966, but the idea did not find its way to implementation. In February 1976, the efforts of Prince Mohammed Al-Faisal and some Sudanese colleagues succeeded in obtaining the approval of the former President of Sudan Jaafar Mohamed Nemiri for the establishment of an Islamic bank in Sudan.
Faisal Islamic Bank (Sudan) was established under the provisional decree No. 9 of 1977 dated 4/4/1977, From the legislature (the People's Assembly at that time)
In May 1977, eighty-six Sudanese and Saudi founders and some citizens of other Islamic countries met and agreed on the idea of establishing and subscribing half of the then-approved capital of six million Sudanese pounds. On August 18, 1977, Faisal Islamic Bank (Sudan) was registered as a limited shareholding company under the Companies Law of 1925. The Bank has officially commenced operations in May 1978.
The law establishing the Bank stipulates that the Bank shall work in accordance with the provisions of the Islamic Shari'a to support the development of society by carrying out all banking, financial, commercial and investment activities, and may, for the purpose of achieving its objectives, establish cooperative insurance companies or any other companies. The law stipulates that the Bank shall have a capital of not less than six million Sudanese pounds. It shall be left to the Foundation's Memorandum and Articles of Association for the distribution of capital shares and the shareholding percentage.
The special law referred to above exempts the Bank from the laws ruling the service and End of Service Benefits provided that the salaries, wages and End of Service Benefits determined by the Bank shall not be less than the minimum stipulated in such laws. The Bank is also excluded from the Insurance Laws and the Law of the NATIONAL Auditor Chamber of 1970 or any law as well as articles no. 32, 44 and 45 of the Law of the Central Bank of Sudan, without conflict with the authority of the Central Bank of Sudan to supervise and direct the Bank's credit policy. The Bank's capital and profits have been exempted from all types of taxes as well as funds deposited with the Bank for investment.
The Bank Objectives
Article (4) of the Articles of Association specifies the objectives of the Bank as follows:
1. To carry out all banking, commercial, financial and investment activities and to contribute to industrial, economic, urban, agricultural, commercial and social projects in any region of the Republic of Sudan or abroad.
2. Accepting deposits of different types.
3. Collection and payment of orders, and other securities of value and dealing in foreign exchange in all its forms.
4. Withdrawal, issuance, acceptance, endorsement, execution of bills and checks whether paid in the Republic of Sudan or abroad.
5. Giving interest-free loans according to the rules determined by the Bank.
6. Trading in precious metals and providing them with safes for the preservation of precious property.
7. Representation of the various banking entities provided that they do not deal with Riba and be committed to the rules of Islamic Sharia in dealing with these banks.
8. Acceptance of deposits from individuals and legal persons, whether for the purpose of saving or investing them.
9. Financing various projects and activities carried out by individuals or legal persons.
10. Opening letters of credit and guarantee, and providing the services required by clients in the financial and economic field and doing the work of investment trustees.
11. Providing banking, financial, commercial and economic investments to customers and providing advice to bodies, individuals and governments on the topics of the Islamic economy, especially Islamic banks.
12. Accepting endowment and donations and directing them according to the wishes of their payers or for the benefit of society as well as accepting Zakat funds and directing them according to the specific Shari'ah principles.
13. Participating in with bodies, companies or institutions that carry out similar activities and cooperating in achieving their objectives in the Republic of Sudan or abroad, provided that this does not involve dealing with Riba or any activity prohibited by law.
14. Establishing institutions or real estate, industrial or commercial activities or companies to assist the Bank in achieving its.
15. Carrying out any work whatsoever the Bank deems necessary or that would enable it to reach all of the purposes set out above or any part thereof or directly or indirectly increase the value of its property, its assets or investments, provided that this is in accordance with Islamic Sharia.
16. The Bank may purchase or, by any other means, acquire all or part of the ownership, fame, rights, actions and privileges of any individual, company or entity and exercise all necessary or appropriate powers to manage such activities.
17. Conducting research and studies related to the establishment of economic projects and employing others for this purpose.
First: The Administrative System
Faisal Islamic Bank (Sudan) is committed to apply a comprehensive quality management system with the vision: "To be the best provider of Islamicfinancial solutions in a contemporary style, by excelling in customer "satisfaction, with creativity and innovation driven by the spirit of youth.
The Bank also identified key success factors as follows:
1. The use of sophisticated systems and techniques to achieve the adequacy of performance control and speed.
2. Selection of qualified staff and the commitment to develop their knowledge, skills, stability and loyalty.
3. Increasing resources as capital and deposits.
4. Implementing an active credit policy that accommodates customers' requirements and attracts new customers.
6. Building widespread and advanced foreign relations.
Second: The Comprehensive Technical Transformation
Since its inception, the Bank has been a pioneer in banking and is now at the top place of providing the most sophisticated banking and information technology building a banking system that adopts state-of-the-art technology in the fields of computers, software and communications. Faisal Islamic Bank (Sudan) is the first bank to become an electronic bank capitalizing on the following copabilities:
1. An internal network was established linking all the branches of the Bank with its headquarters.
2. Electronic connectivity services have been used with international banks through the Swift network to carry out financial transactions in various forms.
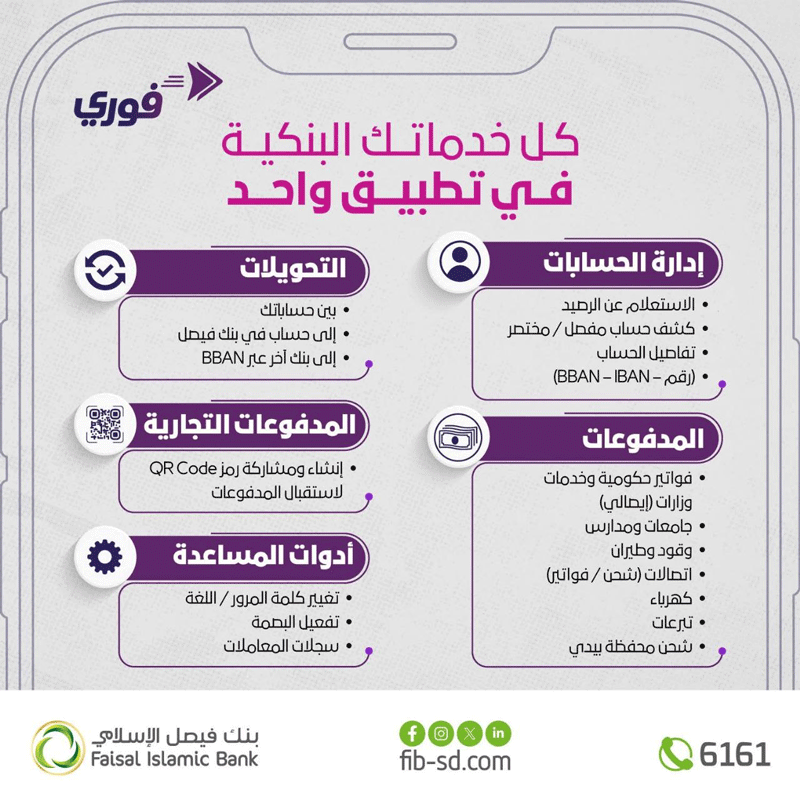
7. The mobile banking.
8. The Bank's branches have been linked to the banking technology projects, such as the Electronic Clearing Project, and the Bank is considered one of the first participating banks.
9. A very large number of ATMs.
10. Points of sale have been established in a large number of shops, to facilitate business transactions for the Bank's customers.